Setting up a GCE Instance as an Inlets Exit Node
The prolific Alex Ellis has a new project, Inlets.
Here’s a quick tutorial using Google Compute Platform’s (GCP) Compute Engine (GCE).
NB I’m using one of Google’s “Always free” f1-micro instances but you may still pay for network *gress and storage
Assumptions
I’m assuming you’ve a Google account, have used GCP and have a billing account established, i.e. the following returns at least one billing account:
gcloud beta billing accounts list
If you’ve only one billing account and it’s the one you wish to use, then you can:
Trendnet TEW-812DRU and DD-WRT
The FBI Portland published an interesting advisory with several, sensible recommendations including firewalling IoT devices from other devices on a home network. I decided to deploy a redundant Trendnet TEW-812DRU version 2.0 for this purpose.
Caveat Developer: Before I go further, I don’t recommend installing DD-WRT on a Trendnet TEW-812DRU unless you’re willing to brick the device irrecoverably.
I read the DD-WRT instructions several times (“peacock thread”,router database – do not use v3.0 beta builds!), thought I’d followed them and still (temporarily) bricked my router using the firmware downloaded from the DD-WRT router database. It is thanks to Justin’s help and his post that I was encouraged to try restoring my device to the Trendent firmware and then retring the DD-WRT installation with an older firmware version.
Google Fit
I’ve spent a few days exploring [Google Fit SDK] as I try to wean myself from my obsession with metrics (of all forms). A quick Googling got me to Robert’s Exporter Google Fit Daily Steps, Weight and Distance to a Google Sheet. This works and is probably where I should have stopped… avoiding the rabbit hole that I’ve been down…
I threw together a simple Golang implementation of the SDK using Google’s Golang API Client Library. Thanks to Robert’s example, I was able to infer some of the complexity this API particularly in its use of data types, data sources and datasets. Having used Stackdriver in my previous life, Google Fit’s structure bears more than a passing resemblance to Stackdriver’s data model and its use of resource types and metric types.
Google Home Exporter
I’m obsessing over Prometheus exporters. First came Linode Exporter, then GCP Exporter and, on Sunday, I stumbled upon a reverse-engineered API for Google Home devices and so wrote a very basic Google Home SDK and a similarly basic Google Home Exporter:
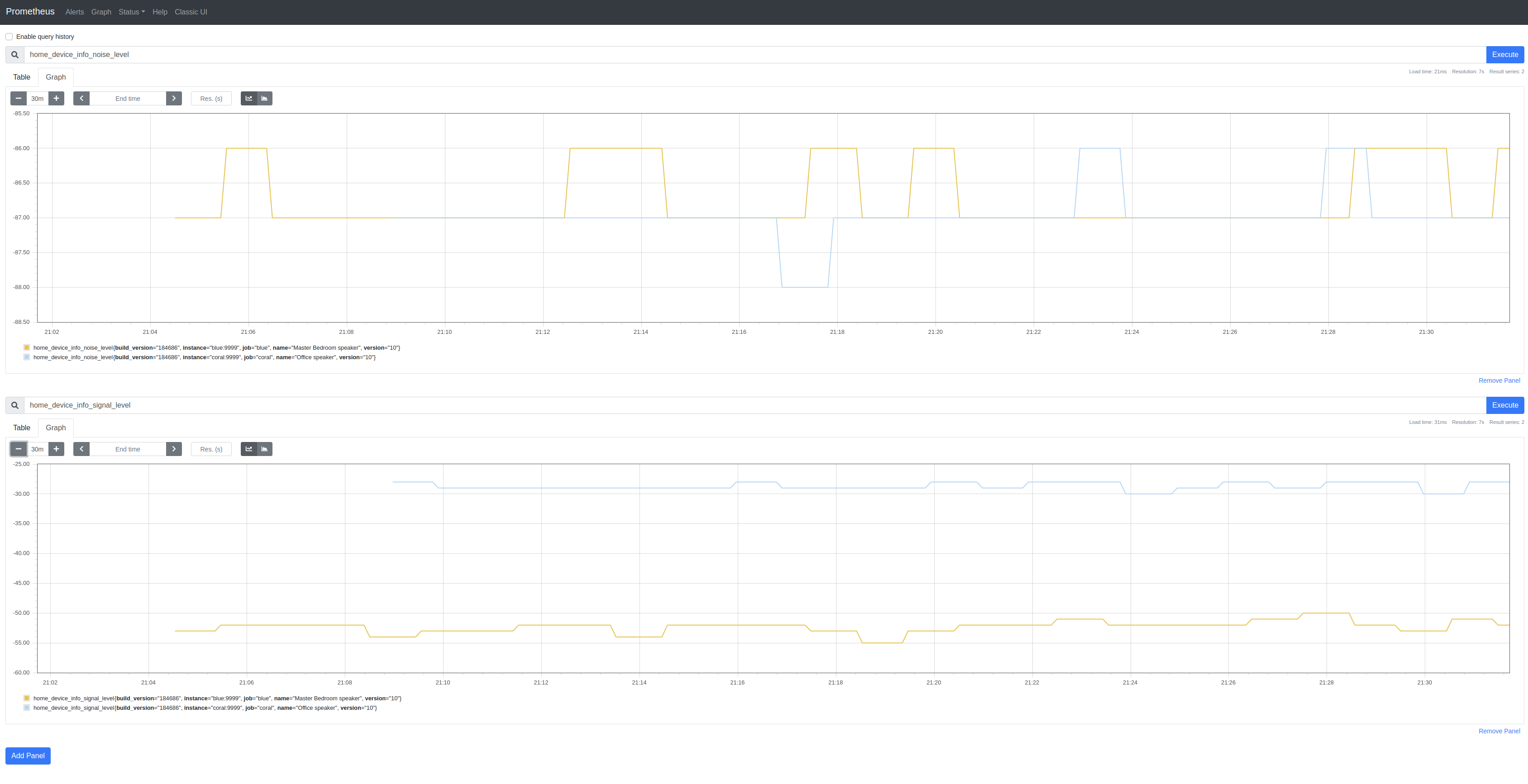
The SDK only implements /setup/eureka_info and then only some of the returned properties. There’s not a lot of metric-like data to use besides SignalLevel (signal_level) and NoiseLevel (noise_level). I’m not clear on the meaning of some of the properties.
Adventures around BPF
I think (!?) this interesting learning experience started with Envoy Go Extensions.
IIUC, Cilium contributed this mechanism (Envoy Go Extensions) by which it’s possible to extend Envoy using Golang. The documentation references BPF. Cilium and BNF were both unfamiliar technologies to me and so began my learning. This part of the journey concludes with Weave Scope.
I learned that Cilium is a CNI implementation that may be used with Kubernetes. GKE defaults (but is not limited to) to Google’s own CNI implementation (link). From a subsequent brief exploration on CNI, I believe Digital Ocean’s managed Kubernetes service uses Cillium and Linode Kubernetes Engine uses Calico.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Exporter
Earlier this week I discussed a Linode Prometheus Exporter.
I added metrics for Digital Ocean’s Managed Kubernetes service to @metalmatze’s Digital Ocean Exporter.
This left, metrics for Google Cloud Platform (GCP) which has, for many years, been my primary cloud platform. So, today I wrote Prometheus Exporter for Google Cloud Platform.
All 3 of these exporters follow the template laid down by @metalmatze and, because each of these services has a well-written Golang SDK, it’s straightforward to implement an exporter for each of them.
Prometheus AlertManager
Yesterday I discussed a Linode Prometheus Exporter and tantalized use of Prometheus AlertManager.
Success:

Configure
The process is straightforward although I found the Prometheus (config) documentation slightly unwieldy to navigate :-(
The overall process is documented.
Here are the steps I took:
Configure Prometheus
Added the following to prometheus.yml:
rule_files:
- "/etc/alertmanager/rules/linode.yml"
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- scheme: http
static_configs:
- targets:
- "alertmanager:9093"
Rules must be defined in separate rules files. See below for the content for linode.yml and an explanation.
Linode Prometheus Exporter
I enjoy using Prometheus and have toyed around with it for some time particularly in combination with Kubernetes. I signed up with Linode [referral] compelled by the addition of a managed Kubernetes service called Linode Kubernetes Engine (LKE). I have an anxiety that I’ll inadvertently leave resources running (unused) on a cloud platform. Instead of refreshing the relevant billing page, it struck me that Prometheus may (not yet proven) help.
The hypothesis is that a combination of a cloud-specific Prometheus exporter reporting aggregate uses of e.g. Linodes (instances), NodeBalancers, Kubernetes clusters etc., could form the basis of an alert mechanism using Prometheus’ alerting.
NGINX Ingress
I’ve written a couple of deployment options (Google Compute Engine; Kubernetes) for an open-source project. The Kubernetes deployment provides NodePort and (TCP) LoadBalancer options and I’ve been trying (unsuccessfully) to add HTTPS Load-balancing.
I should (!) try to deploy to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) but I’ve been using microk8s, Digital Ocean Managed Kubernetes and the Linode LKE Beta. Each of these requires an implementation of Ingress controller. For GKE, GCP’s HTTP/S Load-balancer (GCLB) is used. But, for the other services, NGINX Ingress is a good option and so I’ve been exploring NGINX Ingress (Controller) link. This Ingress appears to work except that I’ve been unable to get it to work with mutual TLS between the (NGINX) proxy and my backend services.
PyPi Transparency Client (Rust)
I’ve finally being able to hack my way through to a working Rust gRPC client (for PyPi Transparency).
It’s not very good: poorly structured, hacky etc. but it serves the purpose of giving me a foothold into Rust development so that I can evolve it as I learn the language and its practices.
There are several Rust crates (SDK) for gRPC. There’s no sanctioned SDK for Rust on grpc.io.
I chose stepancheg’s grpc-rust because it’s a pure Rust implementation (not built atop the C implementation).